Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas and one of the leading causes of lung cancer in the United States. In Michigan, radon exposure is a widespread concern due to the state’s geology, soil composition, and housing stock. While many homeowners search for radon risk by county or ZIP code, the reality is more nuanced — and far more important to understand.
This guide explains how radon risk varies across Michigan, why county and ZIP code data should be used as a reference rather than a guarantee, and what homeowners can do to protect their health.
Why Radon Is a Serious Concern in Michigan
Radon forms naturally as uranium in soil and rock breaks down. That gas moves upward through the ground and can enter homes through cracks in foundations, sump pumps, crawl spaces, and other openings.
Michigan is particularly vulnerable because:
- Much of the state sits on glacial deposits that allow radon to travel easily
- Sandy and gravelly soils are common
- Many homes have basements or crawl spaces
- Seasonal pressure changes increase radon entry during colder months
Because radon is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, testing is the only way to know if a home has elevated levels.
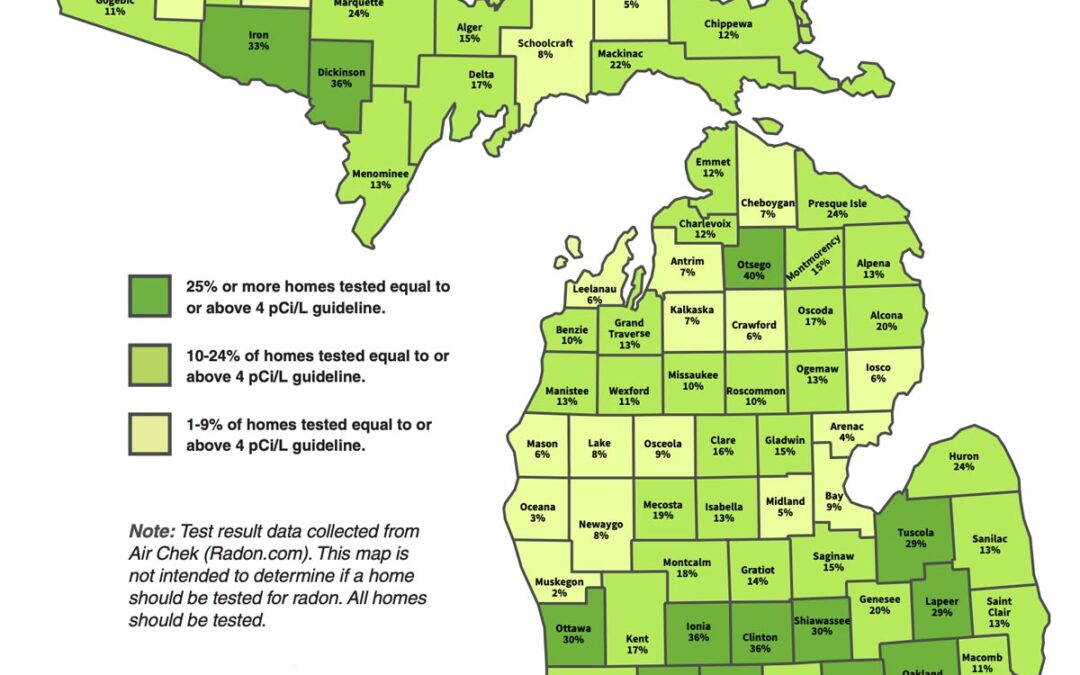
Understanding Radon Risk by County in Michigan
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classifies radon potential by county using three zones:
- Zone 1 (High Risk): Average indoor radon levels above 4.0 pCi/L
- Zone 2 (Moderate Risk): Average levels between 2.0 and 4.0 pCi/L
- Zone 3 (Lower Risk): Average levels below 2.0 pCi/L
Large portions of Michigan fall into EPA Zone 1 or Zone 2, meaning elevated radon levels are common across the state. Counties in Southeast Michigan, Mid-Michigan, West Michigan, and Northern Michigan frequently report homes with levels above the EPA action threshold.
It’s important to understand that EPA zone maps reflect averages, not guarantees. Two homes on the same street can test very differently.
EPA Radon Zones Are a Starting Point — Not a Verdict
County-level radon maps help identify areas where testing should be prioritized, but they do not predict radon levels in an individual home.
Radon levels can vary significantly based on:
- Soil conditions beneath the home
- Foundation type and integrity
- Home design and age
- Ventilation and HVAC systems
Even homes located in lower-risk counties can test above the EPA action level.
Radon Risk by ZIP Code: What Homeowners Should Know
Many Michigan homeowners search for radon risk by ZIP code, especially when buying or selling a home. While ZIP-level data can provide general context, it should not be relied on as a definitive answer.
ZIP code data cannot account for:
- Variations in soil within the same neighborhood
- Differences in foundation construction
- Renovations or additions
- Seasonal airflow and pressure changes
A low radon reading in a nearby home does not guarantee your home is safe.
Why Homes in the Same ZIP Code Can Have Different Radon Levels
It’s common for two neighboring homes to have very different radon readings. Factors that contribute to this include:
- One home having a basement while another is slab-on-grade
- Presence or absence of a sump pump
- Differences in air sealing and insulation
- Soil disturbances from construction or landscaping
Because of these variables, radon testing should always be performed at the individual home level.
Michigan Homes Most Likely to Have Elevated Radon
While any home can have radon, higher levels are more frequently found in:
- Homes with basements or crawl spaces
- Energy-efficient or tightly sealed homes
- Homes with sump pumps or drain tile systems
- Properties built on sandy or gravelly soil
- Homes near lakes, rivers, or glacial deposits
Both older and newer homes in Michigan can be affected.
Why Every Michigan Home Should Be Tested
The EPA recommends taking action if radon levels reach 4.0 pCi/L or higher, but many health professionals advise mitigation even at lower levels when possible.
Key facts every Michigan homeowner should know:
- Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer
- Radon is especially dangerous for non-smokers
- Radon levels can change over time
- Weather, remodeling, and soil movement can impact results
Testing is affordable, non-invasive, and provides peace of mind.
What to Do If Your Radon Levels Are High
If elevated radon is detected, professionally installed mitigation systems are highly effective. Most systems reduce radon levels by up to 99%.
Common mitigation methods include:
- Sub-slab depressurization systems
- Crawl space mitigation and encapsulation
- Sealing foundation entry points
- Proper venting above the roofline
Most systems are installed in one day and require minimal maintenance.
Professional Radon Testing and Mitigation in Michigan
Michigan Radon Control provides professional radon testing and mitigation services throughout Michigan. Our team understands Michigan’s soil conditions, building practices, and regional risk factors.
We offer:
- Residential radon testing
- Real estate radon testing
- Custom mitigation system design
- EPA-compliant installations
- Local expertise you can trust
Schedule a Radon Test for Your Michigan Home
County maps and ZIP code data are helpful tools, but they can’t tell you what’s happening inside your home.
The only way to know your radon risk is to test.
Contact Michigan Radon Control today to schedule your radon test or to learn more about mitigation options for your home.